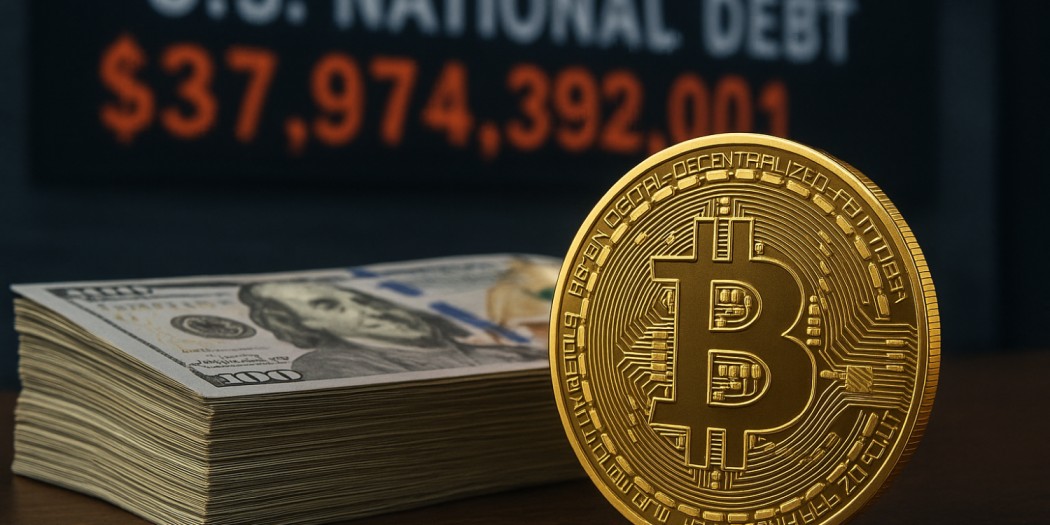
The United States is rapidly approaching an unprecedented milestone — nearly $38 trillion in federal debt. This explosive growth in borrowing has reignited debates about fiscal discipline, economic sustainability, and whether Bitcoin could serve as a hedge or alternative to traditional financial systems. As policymakers grapple with budget deficits and rising interest expenses, crypto advocates are highlighting Bitcoin’s limited supply and decentralized nature as an antidote to unchecked money creation.
The Expanding Debt Crisis
In less than two months, the U.S. government has added roughly $1 trillion to its total debt — a pace that underscores the widening gap between spending and revenue. Of the total federal debt, about 80% is held by the public, including individuals, institutions, and foreign governments. The rest is owed internally between federal agencies.
The U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio now hovers near or above 100%, signaling that the government owes roughly as much as the entire value of the nation’s annual economic output. Rising interest rates have compounded the problem: the cost of servicing this debt now consumes hundreds of billions of dollars each year. Every percentage-point increase in average borrowing costs adds tens of billions in annual interest obligations — creating a feedback loop that widens future deficits.
Several forces are driving this escalation:
- Chronic budget deficits: Federal spending continues to exceed tax revenue year after year, leading to constant borrowing.
- High interest rates: The Federal Reserve’s rate hikes, aimed at curbing inflation, have made new debt far more expensive.
- Stagnant revenue growth: Tax inflows are not keeping pace with surging expenditures.
- Political gridlock: Frequent debt-ceiling standoffs and partisan budget battles undermine investor confidence in long-term fiscal management.
Together, these dynamics have placed the U.S. on a path where debt accumulation outpaces economic growth — a trajectory that economists warn is unsustainable without major policy adjustments.
Market and Economic Implications
Rising Bond Yields
With trillions in new debt supply, investors are demanding higher yields to hold U.S. Treasuries. This surge in yields increases borrowing costs for households, businesses, and the government alike. Large asset managers and economists have described the ballooning debt as one of the biggest systemic risks to U.S. market stability.
Dollar Strength and Inflation Concerns
Although the U.S. dollar remains the world’s reserve currency, rising debt combined with large fiscal deficits raises long-term concerns about inflation and currency devaluation. When governments borrow heavily and central banks indirectly monetize debt, purchasing power erodes. For global investors, this environment heightens the appeal of scarce, non-sovereign assets such as gold and Bitcoin.
Limited Fiscal Flexibility
High interest payments also restrict the government’s ability to respond to future crises. With a growing share of tax revenue allocated to debt servicing, fewer resources are available for defense, healthcare, or infrastructure. In extreme scenarios, the government could face difficult choices between raising taxes, cutting spending, or further expanding the money supply — each with its own economic consequences.
Does This Strengthen Bitcoin’s Case?
The link between debt and Bitcoin’s rising narrative isn’t purely speculative — it’s rooted in economic psychology. As trust in fiat systems weakens, people naturally look for alternatives. Bitcoin, with its fixed supply of 21 million coins, offers a stark contrast to the seemingly limitless creation of government debt.
1. Bitcoin as Digital Gold
Supporters argue that Bitcoin functions like gold in the digital era — a scarce, decentralized store of value that cannot be printed or devalued by political decisions. As the U.S. debt grows, so does the belief that traditional money is losing its reliability. Bitcoin’s predictable monetary policy stands in direct opposition to the flexibility of central banks that can create new currency at will.
2. Hedge Against Monetary Expansion
When governments rely heavily on borrowing, they often resort to inflationary tactics — such as expanding the money supply — to manage debt. Bitcoin’s design is inherently resistant to such manipulation. This makes it appealing to investors seeking protection from long-term currency debasement.
3. Institutional Confidence and Adoption
Institutional participation in Bitcoin has grown significantly. Investment firms, hedge funds, and even some government bodies have begun exploring crypto exposure as part of diversified reserves. This evolution suggests Bitcoin is gradually maturing from a speculative asset into a legitimate macro hedge.
4. Symbol of Monetary Independence
Bitcoin represents financial sovereignty. In an era where individuals fear the consequences of debt-driven inflation or potential capital controls, the ability to hold self-custodied, borderless assets becomes increasingly valuable. The rising debt narrative, therefore, fuels Bitcoin’s ideological appeal as much as its financial one.
Limitations to the Bitcoin Narrative
While Bitcoin’s case as a hedge is compelling, it’s not without flaws. The cryptocurrency remains volatile, often swinging 10–20% in short timeframes. For large-scale investors or governments, such instability can limit its use as a reliable store of value.
Moreover, Bitcoin does not produce income or yield — unlike Treasury bonds, which pay interest. For this reason, it cannot replace government debt as a funding mechanism or as a risk-free asset in traditional finance. Even if the U.S. were to accumulate Bitcoin reserves, the scale of the debt problem dwarfs the potential value of such holdings.
Political and regulatory uncertainty also plays a role. The idea of the U.S. government adopting Bitcoin as a strategic reserve, while symbolically powerful, would face legislative and institutional resistance. Critics argue that fiscal discipline and sound monetary policy — not speculative assets — are the real solutions to the debt crisis.
Broader Economic Risks
Rising debt affects more than just investors. It reshapes the global balance of power. If foreign holders of U.S. Treasuries — such as China or Japan — begin to reduce their holdings, it could trigger a cascade of effects, including higher borrowing costs and weaker confidence in the dollar.
Simultaneously, a loss of fiscal credibility could spark credit rating downgrades, forcing the U.S. to pay even higher rates to attract buyers for its bonds. Inflation expectations might rise again, creating a feedback loop that further strengthens the case for hard assets — including Bitcoin.
What Investors Should Watch
Several key indicators will determine how this story unfolds:
- 10-year and 30-year Treasury yields: Persistent upward movement may indicate market skepticism about U.S. fiscal health.
- Inflation trends: If inflation remains stubbornly high, real interest rates could turn negative, pushing more investors toward Bitcoin.
- Foreign demand for Treasuries: Declining international participation could pressure the dollar and bolster alternative assets.
- Legislative developments: Policy shifts related to debt ceilings, fiscal reform, or crypto regulation could reshape the landscape dramatically.
Investors who believe in the long-term debasement of fiat money often view Bitcoin as an asymmetric bet — small exposure for potentially outsized protection.
Conclusion
The U.S. debt clock’s relentless climb toward $38 trillion serves as a flashing warning sign for both policymakers and investors. It reflects not just fiscal mismanagement but a structural imbalance in how economies are financed. As the burden grows, confidence in fiat systems may continue to erode, nudging individuals and institutions toward decentralized alternatives.
Bitcoin’s story is increasingly intertwined with this macro backdrop. It represents not a replacement for sovereign finance, but a mirror — reflecting the growing distrust in traditional systems and the human desire for financial independence. Whether Bitcoin ultimately becomes a mainstream hedge or remains a niche refuge will depend on how governments respond to the debt crisis unfolding before us.